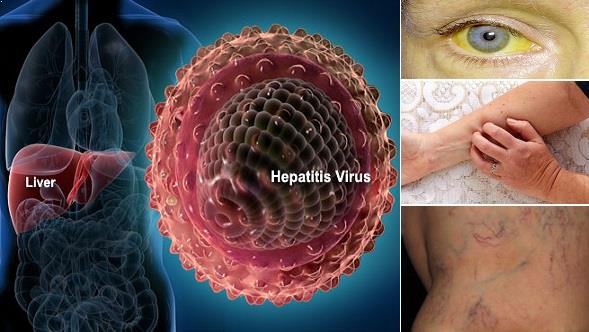
HEPATITIS
There are two types of Hepatitis
- Acute hepatitis - meaning the new onset of Hepatitis
- Chronic hepatitis - meaning the Hepatitis has been present for more than 6 months
What is acute hepatitis?
Acute Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver that results in liver cell damage and destruction. Acute hepatitis is quite common: whereas one in every 4000 people develop acute hepatitis every year in developed countries, this figure may be 5 times higher in developing countries.
Acute Hepatitis Causes
Common causes of acute hepatitis may include:
- Infection with a virus (viral hepatitis A, B, C, D, or E)
- Overdose of drugs (such as acetaminophen, paracetamol)
- Chemical exposure (such as dry cleaning chemicals, and some wild mushrooms)
Acute Hepatitis Symptoms
The following are the most common symptoms of acute hepatitis: jaundice, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, fever, tenderness in the right upper part of the tummy (abdomen), sore muscles, joint pain and itchy red hives on skin.
Acute Hepatitis Diagnosis
- Specific laboratory tests for virus detection
- Liver function tests
What is chronic hepatitis?
Some people do not recover fully from acute hepatitis and develop chronic hepatitis, as the liver continues to sustain more damage and inflammation. Hepatitis is considered chronic if symptoms persist longer than six months. Chronic hepatitis can last years.
Different forms of chronic hepatitis
- Alcohol-induced chronic hepatitis - continued damage throughout the liver from heavy alcohol consumption.
- Chronic active hepatitis - an aggressive inflammation and destroyer of liver cells, which may lead to cirrhosis.
- Chronic persistent hepatitis - a milder chronic inflammation of the liver, which usually does not lead to cirrhosis.
Chronic Hepatitis Causes
Certain viruses and drugs may cause chronic hepatitis in some people, but not in others.Common causes include:
- Viral hepatitis
- Heavy alcohol consumption
- Autoimmune disorder (when the body attacks its own tissues)
- Metabolic disorders (such as Hemochromatosis or Wilson's Disease)
- Reaction to certain medications especially those given for TB.
Chronic Hepatitis Symptoms
Symptoms for chronic hepatitis are usually mild. Some individuals may experience no symptoms, while others may experience the following: feeling ill, poor appetite, fatigue, low fever, upper abdominal pain, jaundice, symptoms of chronic liver disease (such as enlarged spleen, spider-like blood vessels in skin and fluid retention).
Chronic Hepatitis Diagnosis
In addition to a complete medical history and medical examination, diagnostic procedures for chronic hepatitis may include a) laboratory tests for specific viruses, b) liver function tests or c) liver biopsy to determine severity of inflammation, scarring, cirrhosis and underlying cause.
Chronic Hepatitis Treatment
The goal of treatment is to stop damage to the liver and alleviate symptoms. Treatment may include one/more of the following:
- Antiviral Agents & antibody preparations
- Corticosteroids
- Discontinuation of the causative drugs/agent
- Discontinuation of alcohol
The prevention of Hepatitis B and C should be aimed at the high risk groups and situations which are a) Unsafe Blood transfusion, b) Hepatitis B or Hepatitis C in the family, c) Surgical procedures or dental manipulation, d) intravenous drug abuse, e) Unprotected sexual exposure, f) Dialysis, g) Medical or paramedical personnel. The prevention strategies include vaccinations & antibody preparation